Observer observes a certain similarity-of-forms, a certain "morphism", between organic entities known as "trees" and structures of the digital realm.
Observer observes a certain similarity-of-forms, a certain "morphism", between organic processes known as "germination, differentiation, growth and decay" and processes taking place in the informatic realm.
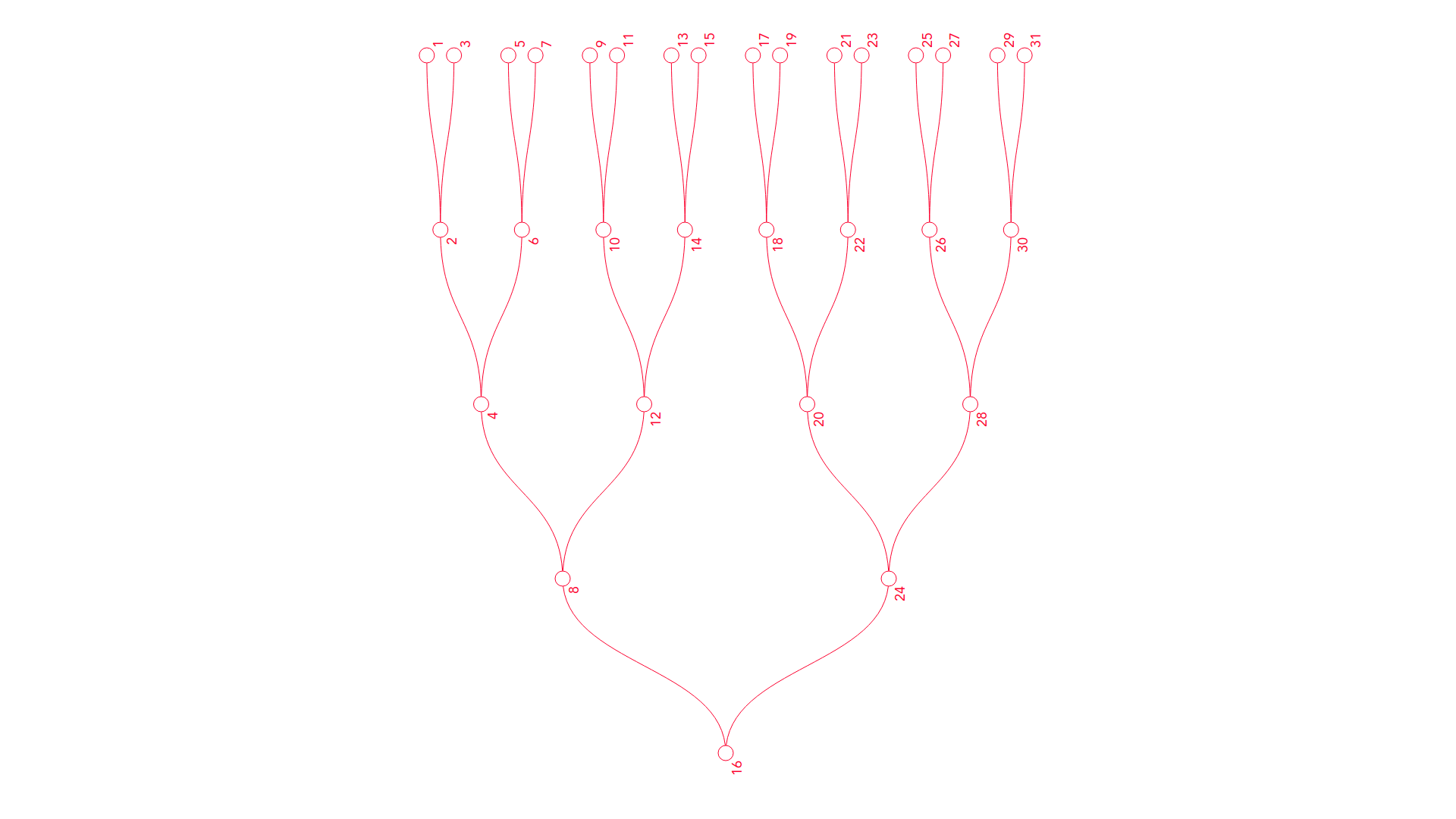 You will be divided into break-out rooms in which You will play the "number guessing game". Game goes like this:
You will be divided into break-out rooms in which You will play the "number guessing game". Game goes like this:
one person chooses, in his|her mind only a number N between 0 and 31
other start at node 16 and ask "is N smaller than 16?" ... if the answer is "yes", You will take the upper/left road leading to number 8 ... if the answer is "no", You will take the lower/right road leading to number 24
now You ask, "is N smaller than 8?" (or 24)...again, if the answer is "yes", You take the upper/left road (leading You to 4, resp. 20), in other case You take the lower/right road (leading You to 12, resp. 28)
You repeat two more times until You reach the leaves of the tree....if N is odd, the leaf node where You finished is the number N
(if number N is even, than it is one of those numbers which You traversed on Your path, e.g. 16,24,20 or 22 if You ended up at leaf 23)
then another person invents the number and others guess.
P.S. this binary tree will help You : https://kastalia.medienhaus.udk-berlin.de/7815
- One person chooses some well known animal or plant.
- The others try to guess it, they can only ask Yes / No questions. (e.g. Do You live in a forest ? Are You rooted ? Do You have four legs ? Do You fly ? etc.)
- The one who guesses is the one who chooses the animal/plant entity for the next round.
- How many rounds can You do in 10 minutes ?
- Break-out room, 15 minutes
- Collaborative ASCII or whiteboard screenshots highly appreciated.
root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. It is also referred to as the root account, root user and the superuser.
Root privileges are the powers that the root account has on the system. The root account is the most privileged on the system and has absolute power over it (i.e., complete access to all files and commands). Among root's powers are the ability to modify the system in any way desired and to grant and revoke access permissions (i.e., the ability to read, modify and execute specific files and directories) for other users, including any of those that are by default reserved for root.
The word root also has several additional, related meanings when used as part of other terms, and thus it can be a source of confusion to people new to Unix-like systems.
One of these is the root directory, which is the top level directory on a system. That is, it is the directory in which all other directories, including their subdirectories, and files reside. The root directory is designated by a forward slash ( / ).
Another is /root (pronounced slash root), which is the root user's home directory. A home directory is the primary repository of a user's files, including that user's configuration files, and it is usually the directory in which a user finds itself when it logs into a system. /root is a subdirectory of the root directory, as indicated by the forward slash that begins its name, and should not to be confused with that directory. Home directories for users other than root are by default created in the /home directory, which is another standard subdirectory of the root directory.